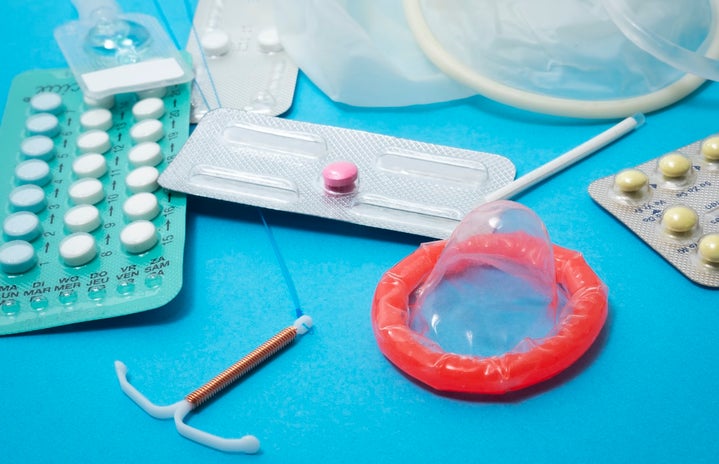
Getting frisky can be…risky. Whether you use condoms or rely on the pull out method, the chance of pregnancy is slim but never. Within a year, the chance of getting pregnant without any form of birth control is 85% according to Planned Parenthood.
There’s only one birth control method to date that is 100% effective. Abstinence. I know what you’re thinking, just because it’s the most effective method, doesn’t make it the most practical. And you’re right. Abstinence isn’t the easiest practice, but it’s also not the only capable birth control method available.
There are so many different types of birth control. Some are more effective than others and others even have certain health benefits. Hormonal birth control can ease period symptoms or even eliminate periods all together.
Below is a list of birth control ranked from most effective to least. The information below is provided by the following: Health Partners, Health.gov, Nationwide Children’s, and Planned Parenthood.
The Implant:
A matchstick sized rod, that is implanted in the upper inside of the arm. The implant releases the hormone progestin which thickens the mucus of the cervix, trapping sperm from moving and stopping eggs from being released from the ovaries—thus preventing pregnancy. This method is effective for up to five years with 99% accuracy and can be removed at any time. This method has increased in popularity because it leaves little room for error. No more daily pills or going to a doctor every month for a refill, just “get-it-and-forget it”.
Pros
-eases period pain (1 in 3 women don’t get a period after 1one year)
-estrogen free (for those who cannot use estrogen-based products)
-reversible, can get pregnant after removal
-very effective, little room for error
-effective for up to 5five years
-Discrete
Cons
-six to 12 months of spotting
-headaches
-breast pain
-nausea
-weight gain
-bruising or infection at the implant sight
-does not protect again or prevent the spread of STDs
Cost?
It could cost between $0 – $1,300 a year depending on insurance and geographic location.
The IUD:
A T-shaped inter-uterine device that is implanted by your doctor. This method is effective for eight to 12 years and can even be used as an emergency contraceptive, preventing pregnancy for up to 5five days after unprotected sex. There are 2 types of IUDs: the hormonal IUD and the copper IUD. Both IUDs change the way sperm move, preventing access to the eggs, thus preventing pregnancy.
The hormone in the hormonal IUD-much like the hormones in the implant- thicken the mucus of the cervix, blocking and trapping sperm. The hormone prevents ovulation, stopping eggs from leaving the ovaries for fertilization. The copper IUD works because sperm do not like copper. The sperm try to avoid the copper IUD and find another route to the eggs and get trapped. Another “get-it-and-forget it” contraceptive that many regard as “mistake proof”. This method is also 99% effective.
FDA Approved IUDS
Mirena, Kyleena, Liletta, and Skyla (hormonal)
Paragard (copper)
Pros
-eases period pain (some women stop getting period all together)
-reversible, can get pregnant after removal
– (copper IUD) doesn’t have hormones
-can be used as an emergency contraceptive
-99% effective
-effective for three to 12 years
-Discrete
Cons
-three to six months for side effects to subside
-can slip out
-backaches
-should not use menstrual cup with this form of birth control
-risk of ectopic pregnancy
-risk of bacterial infection at time of insertion
-could push through uterus
-insertion can be painful
-(copper IUD) heavier, more longer periods
-(copper IUD) worst cramping of all options
-does not protect again or prevent the spread of STDs
-spotting or cramping after removal
Cost?
It could cost between $0 to $1,300 a year depending on insurance and geographic location.
The Shot:
The Ddepo shot is a quarterly injection that prevents pregnancy by preventing ovulation. It thickens cervical mucus preventing sperm and egg from meeting. You get the shot 3-4 times a year and the shot is 94% effective—best results when paired with condoms.
Pros
-94% effective
-only need to be taken quarterly (3 to 4 times a year)
–Discrete
-less period pain (half of users stop getting a period after a year)
-can protect against ectopic pregnancy and uterine cancer
-the shot Iis temporary so you can stop anytime between shots
Cons
-bleeding more than usual
-spotting
-nausea
-weight gain
-headaches
-sore breasts
-depression
-bruising at shot sight
-permanent dent in skin at shot sight
-can take up to ten months to get pregnant after stopping
Cost?
It could cost between $0-$150 per shot depending on insurance and geographic location.
The Patch:
The transdermal contraceptive patch, like the shot, prevents pregnancy by stopping ovulation. Like other hormonal contraceptives, the patch, thickens cervical mucus preventing sperm and egg from meeting which prevents fertilization. You wear the patch on either the stomach, buttocks, back, or upper arm. The hormones—estrogen and progestin—are absorbed through the skin using the patch. This method is 91% effective.
Pros
-effective (when used properly)
-more convenient than daily pills
-eases period pain
-prevents bone thinning
-prevents ovarian cysts and breast cysts
-lighter periods
-lessens/prevent acne
-prevents ectopic pregnancy
-prevents ovarian cancer
-prevents serious infections of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus
-prevents PMS (premenstrual syndrome)
-prevents iron deficiency
-can get pregnant after stopping use
Cons
-needs to be changed weekly
-spotting
-changes in periods
-skin reactions at patch sight
-nausea
-breast pain
-headaches
-increased risk of stroke, heart attack, blood clots and liver tumors
-increases side effects if over the age of 35 and smokes
Cost?
It could cost between $0-$150 per use depending on insurance and geographic location.
The Pill:
The pill is one of the oldest forms of birth control. You take one pill a day to prevent pregnancy. There are 2 types of birth control: combination pills, and Progestin only pills. The estrogen free pill is commonly recommended for those who smoke or are over 35. Like most other birth control methods, the pill, stops ovulation to prevent the fertilization of the egg. This method is 91% effective, when used on schedule and consistently.
Pros
-can help with period pain
-can clear acne
-lower risk of ectopic pregnancy
-prevent bone thinning
-prevents ovarian and mammary cysts
-prevents infections of female reproductive organs
-lessens PMS (premenstrual syndrome)
-can get pregnant right away after stopping
Cons
-must take pill daily
-spotting or bleeding between periods
-headaches
-nausea
-sore breasts
-irregular period for 2-3two to three months
-missing pills can lead to pregnancy
-doesn’t protect against STDs or prevent the spread of STDs
Cost?
It could cost between $0-$50 a month depending on insurance and geographic location.
The Ring:
This Ring is a small flexible plastic ring that goes inside the vagina. The ring constantly releases hormones in the body that prevent pregnancy. There are 2 kinds of rings: the NuvaRing and the Annovera., both Both are 91% effective.
Pros
-convenient
-can help with period pain
-can clear acne
-lower risk of ectopic pregnancy
-prevents bone thinning
-prevents ovarian and mammary cysts
-prevents infections of female reproductive organs
-lessens PMS (premenstrual syndrome)
Cons
-nausea
-breast pain
-headaches
-spotting
-changes in periods
Cost?
It could could between $0-$200 a year depending on insurance and geographic location.
Diaphragms:
A shallow, bendable cup that goes inside the vagina and covers the cervix. When paired with spermicide, the diaphragm is much more effective. The chemicals in the spermicide stop sperm from moving and the diaphragm keeps the spermicide in place.
Pros
-doesn’t interrupt sex
-no hormones
-no side effects
-lasts a long time (up to two years)
-convenient
Cons
-must use every time you have sex
-hard to use correctly (especially if first time)
-no one size fits all
-spermicide has side effects
Cost?
It could be between $0-$75 $250 a year depending on insurance and geographic location.
Cervical Cap:
A small silicone cup that goes inside the vagina, covering the cervix. Much like the diaphragm, the cervical cap prevents sperm from entering the cervix by acting as a barrier between sperm and egg. When paired with spermicide the cervical cup keeps the spermicide in place while the chemicals in the spermicide, kill the sperm before they meet the egg.
Pros
-doesn’t interrupt sex
-no hormones
-no side effects
-last a long time (up to a year)
-convenient
Cons
-must use every time you have sex
-hard to use correctly (especially if first time)
-no one size fits all
-spermicide has side effects
Cost?
It could cost between $0-$275 a year depending on insurance and geographical location.
Spermicide and contraceptive gel:
A chemical birth control that you put in the vagina before sex to stop sperm from entering and eggs from leaving.
Generally, you do not need a prescription for spermicide but some vaginal contraceptive gels, like, Phexxi, require a prescription. This method is only effective when paired with the cervical caps or diaphragms.
Pros
Missing information
Cons
-must use every time you have sex
-spermicide has side effects
-messy
-doesn’t protect against STD’s
Cost?
It could be between $0- $270 a year depending on insurance and geographical location.
Male Condoms:
These are thin sleeves that cover the penis during sex. They are 85% effective, but when paired with other methods they can be more effective. There are 3 types of condoms: latex, plastic, and lambskin. Latex condoms are made of rubber and protect against pregnancy and STDs. It’s best to only use water-based lubricant with latex condoms because oil-based lubricant could damage the condom. Plastic condoms are recommended for those with latex allergies. You can use water-based or oil-based lubricant, but if you’re not sure, check the directions on the package. Lambskin condoms are another good alternative for those with latex allergies. They are effective in preventing pregnancy, but not STDs. This is because there are tiny holes in lambskin condoms that are small enough to stop sperm but not bacteria.
Pros
-protect against STDs
-85% effective
-very accessible, no prescription needed
-easy to use
-cheap
Cons
-you must use condoms every time you have sex
-takes away feeling
-could cause discomfort
Cost?
It could cost between $0- $30 a pack depending on where you purchase them from.
There’s no perfect birth control method but knowing your options is the first step in preventing pregnancy. For more information about birth control, you can talk to a nurse practitioner in the Henry Wise Wellness Center or talk to your primary care physician. Planned Parenthood also has a lot of information on their website, or you can schedule a Telehealth visit to answer any other questions you may have about birth control and the best option for you.